Overview
Tubal ligation is an ideal choice for women who are certain they don't want more children. This procedure offers a permanent long-term solution and reduces dependency on short-term methods such as tablets or intrauterine devices, it serves a crucial role in family planning. For many women, especially those in underserved or rural areas, tubal ligation is a practical choice when consistent access to healthcare or contraceptive supplies is limited.
Contraception is a choice and a responsibility that are strongly related to social and economic well-being in cultural contexts where women often become the responsibility bearer. Dialogue on gender roles in family planning and contraception are sparked by contrasting it with vasectomy, a more simple male sterilization procedure, which emphasizes the significance of shared responsibility in reproductive health.
Let's explore the tubal ligation procedure, recovery, effectiveness, and overall impact on everyday living to determine which one is more effective and why.
What is Tubal Ligation?
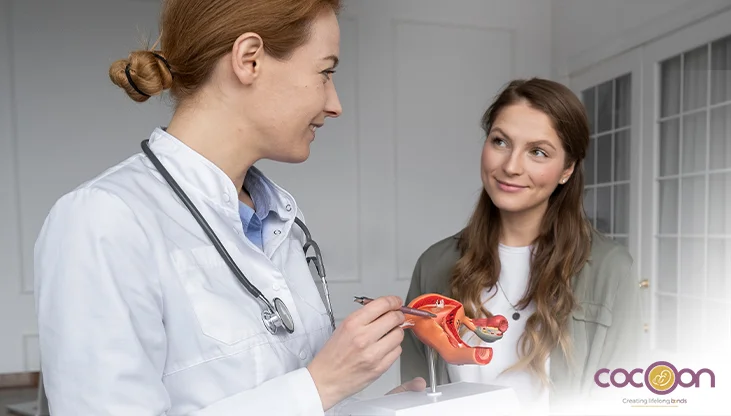
Tubal ligation, commonly referred to as "getting your tubes tied," is a surgical procedure designed to permanently prevent pregnancy. It works by cutting, blocking, or sealing the fallopian tubes, which stops sperm from reaching and fertilizing an egg. The term "tubal" refers to the fallopian tubes, while "ligation" means "tying." During the procedure, the tubes may be closed off using clips, bands, clamps, or by cutting and tying them with a special surgical thread (suture). As a permanent form of birth control, tubal ligation is about 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. It's a safe and straightforward option for women who are sure they don’t want to become pregnant in the future, allowing them to enjoy intimacy without the worry of unintended pregnancy.
What are the Side Effects of Tubal Ligation?
Even though tubal ligation is normally safe and well tolerated, there are risks and side effects associated with it, as with any other surgical procedure. While most side effects are mild and short-term, others may require medical attention. Common and possible side effects are:
- Pain After Procedure: Following the surgery, some women may have slight shoulder discomfort, bloating, stomach pain, or fatigue, these side effects often go away in a few days.
- Altered Menstrual FLow: Following the treatment, some women report heavier or irregular periods, although research indicates that these changes are often coincidental and unrelated.
- Internal Bleeding or Infection: Like any surgery, there is a little chance of internal bleeding or infection at the site of the incision, although these are rare if the procedure is carried out in a clean, controlled setting.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Although it is rare, ectopic pregnancy—a medical emergency that happens when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube—is more likely to occur if pregnancy develops after tubal ligation.
- Side Effects Associated with Anesthesia: General or local anesthesia may cause nausea, vertigo, or allergic responses in certain people.
- Emotional Distress: Some women could experience sadness, particularly if they made the choice under influence or at an emotionally difficult time. Women who are younger or want more children are more likely to experience this.
- Post-Tubal Ligation Syndrome (PTLS): Women with this contentious and undefined disorder report post-procedure symptoms such as discomfort, irregular menstruation, or hormonal abnormalities. However, there isn't much scientific proof to prove that this syndrome is associated with tubal ligation.
What is Involved in Tubal Ligation Reversal?
Following tubal ligation (tying your tubes), a procedure known as tubal ligation reversal releases your fallopian tubes. Restoring your fertility might be a possibility if you decide to carry pregnancy. You can get advice on whether this procedure is suitable for you from your doctor. In the event that reversal is not possible, they might discuss other options with you, such as IVF. Tubal ligation reversal is surgery is a surgical procedure performed to undo the tubal ligation. In order to facilitate conception, a tubal ligation reversal reopens or reconnects your tubes, allowing sperm and eggs to fertilise. You can get pregnant again by reversing a tubal ligation. Tubal ligation reversal is also known as tubal reversal, tubal reanastomosis, and tubal sterilization reversal.
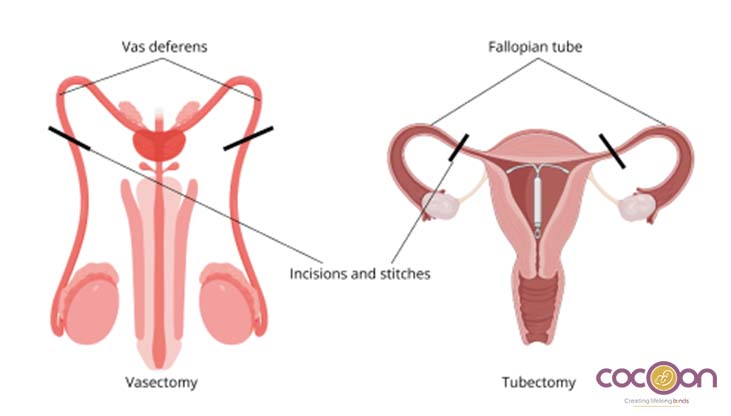
Tubal Ligation vs. Vasectomy
| Feature | Tubal Ligation | Vasectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Who undergoes the procedure? | Women | Men |
| Procedure Type | Surgical blocking/sealing of fallopian tubes | Surgical cutting/sealing of vas deferens |
| Invasiveness | More invasive (requires general or local anesthesia) | Less invasive (usually done under local anesthesia) |
| Duration of Procedure | 20–30 minutes (often laparoscopic) | 10–15 minutes |
| Hospital Stay | Usually day-care; sometimes 1-day observation | Outpatient (same-day discharge) |
| Recovery Time | Few days to a week | 1–2 days |
| Effectiveness | Over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy | Over 99.8% effective after semen clears (within 3 months) |
| Reversibility | Possible but less successful and more complex | Possible with higher success rates than tubal reversal |
| Risks/Complications | Infection, bleeding, ectopic pregnancy (rare) | Infection, mild pain/swelling (rare) |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Less expensive |
Vasectomy is usually the better option for couples in seeking permanent contraception between tubal ligation and vasectomy because it is less invasive, less risky, heals quicker, and is cheaper. However, the decision should be made jointly based on mutual consent, consideration of long-term reproductive objectives, personal comfort, and medical fitness should guide the choice.
Conclusion
Tubal ligation is an effective, safe, and permanent method of preventing pregnancy. If you have had a tubal ligation and would now like to conceive, tubal ligation reversal might be available for you. Your surgeon will decide if you are a right candidate for surgery before proceeding with it. How healthy your fallopian tubes are and how old you are will determine if reversal is an option or if IVF would be a more viable option. In general, vasectomy is less complicated, safer, and more expensive than tubal ligation.
It has a shorter recovery period and fewer risks. When both spouses are willing, vasectomy is the recommended course of action for couples thinking about permanent contraception.
Discuss with your doctor about what course of action is best for you and what to expect during and after the surgery. Book appointment & talk to our experts at Cocoon Hospital for personalised advice.
Frequently Ask Questions:
Q1: How successful is tubal ligation?
A: It is one of the most reliable methods of long-term birth control. It has an over 99% success rate in preventing pregnancy.
Q2: Is the tubal ligation procedure painful?
A: You won't experience any discomfort during surgery because it is performed under anaesthesia. Little pain or cramps can occur during recovery which normally go away in a few days.
Q3: What is the duration of the recovery period after tubal ligation?
A: Depending on their health and the kind of surgery, most women recover in a few days to a week and can resume their regular activities soon after.
Q4: What is the Cost of Tubal Ligation in India?
A: In India, tubal ligation usually costs between ₹20,000 and ₹40,000, depending on the city, hospital, and surgical technique. Under national family planning programs, the operation is facilitated by government hospitals at a reduced cost or even free of cost.