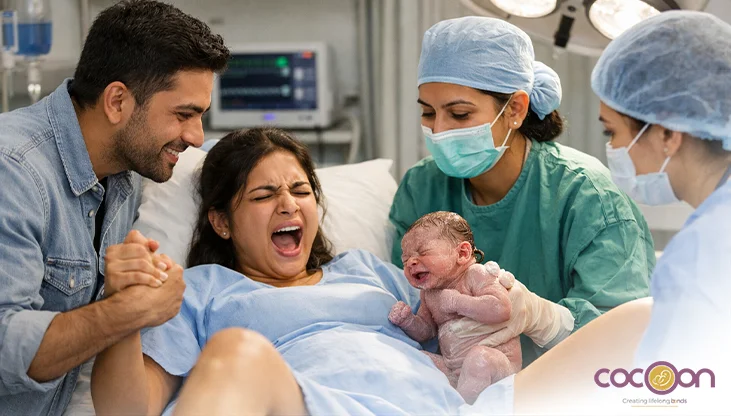
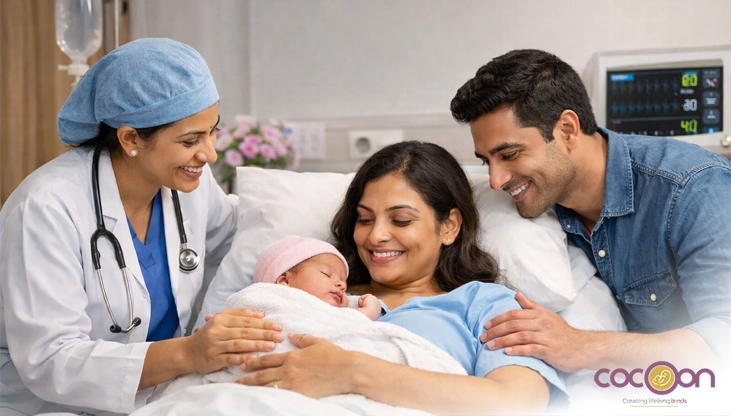
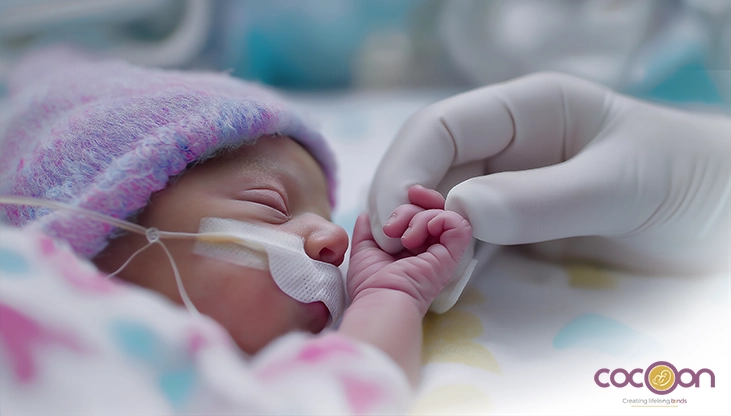
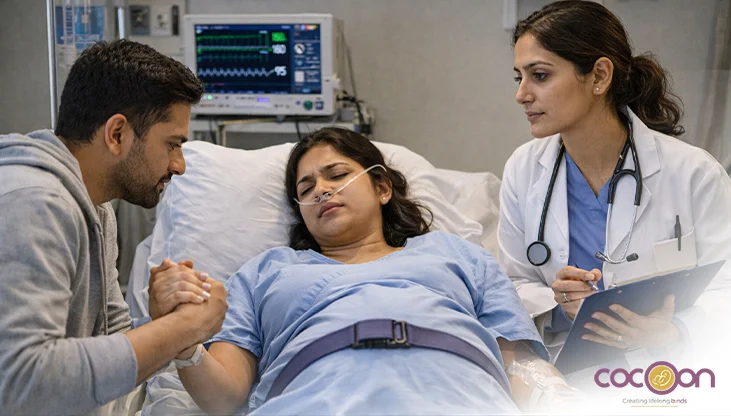For the health of your unborn child, it is desirable to have a full-term pregnancy. The average length of a full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks. Preterm or premature birth occurs when a baby is born before 37 weeks. Early birth can result in health issues for the rest of a baby's life.
The likelihood of early labour is higher for some women. Premature babies are more prone to go into labour early, as do women with a short or weak cervix (the lowest portion of the uterus that links to the vagina). In these situations, the doctor could suggest progesterone or cerclage therapy as remedies. Progesterone can be administered vaginally or as an injection. For women with a short cervix or a history of premature birth, it can help reduce the likelihood of an early labour.
The cerclage technique helps prevent premature birth by closing a woman's cervix with stitches. For women who have miscarried or had premature babies, have a short cervix, or have a cervix that opens (dilates) too soon, doctors may advise cerclage.
Additionally, there is a higher chance of early labour for women carrying twins. When carrying more than one fetus, these therapies cannot stop early labour. Mothers should contact their midwife or doctor immediately if they believe they are in labour or if they are experiencing contractions, such as cramps or stomach pains. You should go to the hospital immediately if you have any bleeding or if your water bursts (which can be a continuous leak, an intermittent leak, or a gush of fluid).
Going to a hospital with the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is the best option if labour begins early. NICU-equipped hospitals specialise in managing premature infants. Regular prenatal care increases a woman's chances of having a healthy pregnancy as well as a baby.
Read Also: Prenatal Care Tips Every Expecting Parent Should Follow
What is Premature Birth?
A baby born too early, roughly three weeks ahead of its due date, is referred to as a preterm, premature, or "preemie." About 40 weeks are needed for full-term pregnancy (fetal development). A baby delivered at 37 weeks or earlier is considered preterm. An infant delivered prematurely or early may be at major risk for health problems. This is because in the final few weeks of pregnancy numerous organs, including the liver, lungs, and brain, are still developing.
A newborn can be:
- Late preterm: Babies born between 34 and 36 weeks of pregnancy.
- Moderately preterm: Babies born between 32 and 34 weeks of pregnancy.
- Very preterm: Babies born between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy.
- Extremely preterm: Babies born before 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Read Also: Importance of Antenatal Care
What are the Symptoms of Premature Birth?
An infant who was born prematurely may not show any obvious signs. However, some of the most prevalent signs of premature birth are:
- Low birth weight
- Low body temperature
- Breathing difficulties
- Feeding difficulties
- Fine hair (lanugo) covering the baby’s body
What are the Causes of Premature Birth?
Premature deliveries can occur unexpectedly and without a specific cause. For medical reasons, doctors may induce (start) labour early in some circumstances. Premature labour can be caused by:
- Chronic health conditions, like diabetes or heart disease
- Placental conditions like placental abruption or placenta previa.
- Expecting multiples (around 60% of twins and triplets are born prematurely)
- Preeclampsia
- Complications of uterus or cervix
- Vaginal bleeding or infections during pregnancy.
- Substance abuse
- Smoking
What are the Treatment Options for Premature Birth?
Preterm newborns often need specialised medical treatment in the NICU. This is a special section of the hospital for babies that require specific care and medical attention. Some babies may spend weeks or months in the NICU. Preterm newborns usually need care for:
- Breathing
- Maintaining their own body temperatures
- Feeding
- Gaining weight
Preterm labour does not always result in a birth. Labour may cease on its own or with the appropriate therapies. If you go into preterm labour, your doctor may prescribe drugs to stop or postpone the process. If those treatments do not work, other medications may help prepare the baby for birth to prevent certain medical issues.
Read Also: Neonatal Care Tips for New Parents: What to Expect in the NICU?
What are the Prevention Tips for Preterm Birth?
There is not one solution for preventing premature birth, however you can minimise your risk with the following actions:
- Quit alcohol, smoke, and other drugs during pregnancy.
- Consume wholesome, balanced meals when pregnant.
- Start prenatal care right from the first trimester so that your obstetrician can detect health risks as early as possible.
- Talk to your doctor about managing illnesses such as diabetes and high blood pressure as preterm birth and other difficulties might result from untreated medical disorders.
- Do not miss your appointments for prenatal care.
- Manage your stress levels.
- Wait at least 18 months to plan the next pregnancy.
What is the Future Outlook for Preterm Birth?
Premature babies have a fair chance of being healthy adults, particularly if they were born after 34 weeks of pregnancy. A baby's risk of developing health issues that could impact them later in life increases with the time of birth. No, having an early birth does not make your child disabled. It merely raises your chance of developing some problems. If you're experiencing difficulties controlling a medical condition such as diabetes, hypertension, or preeclampsia, get in touch with your doctor. Your doctor will work with you to manage preterm delivery, which may prolong the pregnancy to prevent an early delivery.
Conclusion
Premature birth can cause major health issues to a newborn. When an infant does not have enough time to develop in the uterus, vital organs may not fully mature. However, innovations in neonatal care are assisting many preterm infants in developing into healthy and strong children. Attending all of your prenatal visits, managing any underlying health concerns, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy are the most effective ways towards preventing premature birth. Always disclose your complete medical history with your doctor so that they can provide the best treatment for you during pregnancy.
Get expert gynecologist’s advice on preterm labor risks, medical care, and tips for a healthy pregnancy at Cocoon Hospital. Book your consultation now!
FAQs
Q1: What is the treatment for premature birth?
A: Treatment may involve NICU care, respiratory support, medications, and incubators for temperature regulation.
Q2: How to prevent premature birth?
A: Regular prenatal care, managing health conditions, and a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk.
Q3: What are the causes of premature birth?
A: Common causes include multiple pregnancies, infections, chronic conditions, lifestyle factors, and previous preterm births.