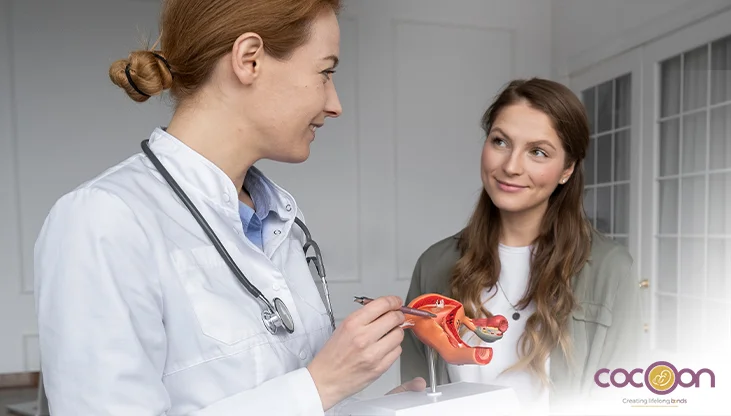
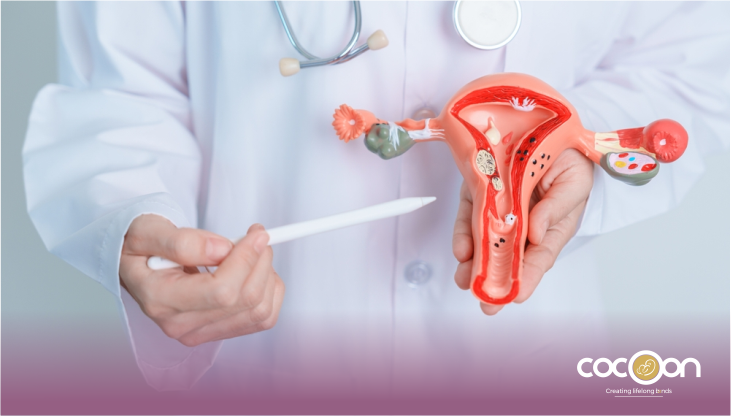
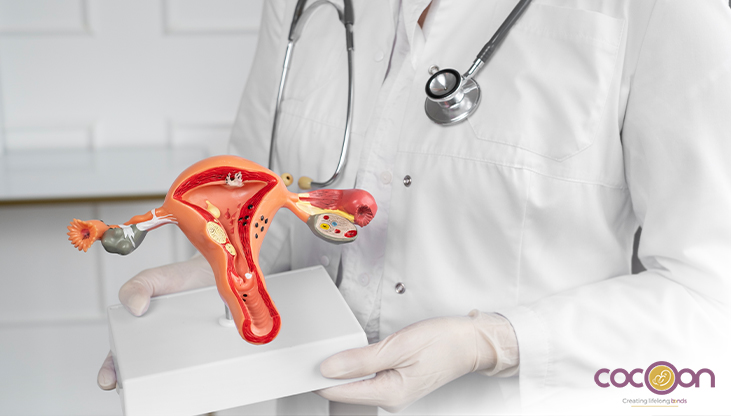
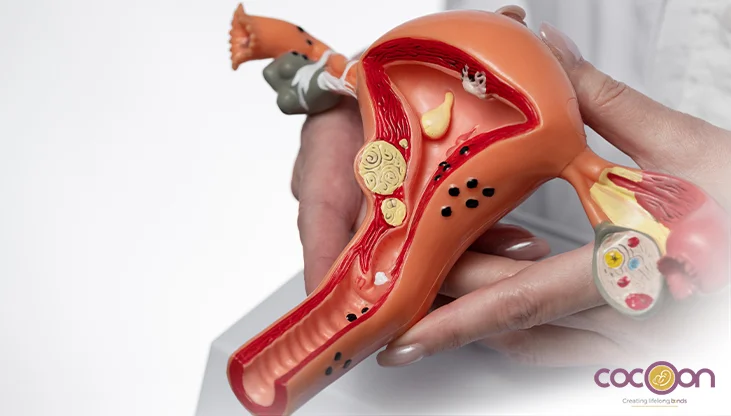
Abnormal uterine or ovarian growth may occur in several forms. Owing to the similarity of symptoms and type of growth, the conditions may also be misinterpreted. For instance, ovarian cyst symptoms often are like uterine fibroids. For an accurate treatment, knowing or understanding the key differences between the two is important.
Since both ovarian cysts and fibroids are critical conditions, a lack of treatment may lead to additional health complications and deteriorate reproductive health. Each growth whether of cyst or fibroid can be essentially managed through precise monitoring and treatment from a gynaecologist.
In this article, we will talk about the two conditions viz. cysts and fibroids, their key differences, and when should you seek medical advice. Let us have a look.
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
As the name suggests, ovarian cysts refer to an abnormal growth in or on the ovaries. These growths are often non-cancerous and include fluid-filled sacs. Often, the signs of ovarian cysts may not be apparent for some women while the symptoms can be quite disruptive for others.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids refer to muscular growth that develops in the uterine lining, uterine cavity, or on the uterus. If left untreated, the small fibroids may continue to grow and cause health complications. Hence, fibroid removal is recommended to prevent it from disrupting reproductive health.
Ovarian Cysts vs. Fibroids: Symptoms
Cysts and fibroids may not always show symptoms from the beginning. In fact, a lot of women may not even realize until the gynaecologist discovers the condition during a routine exam. If, however, the condition is left untreated, the cysts and fibroids may become large, and start showing a variety of symptoms.
Signs of Ovarian Cysts
Cysts are usually half an inch to 4 inches in size or larger. These may cause:
- Ovarian cyst pain is characterized by a sharp pain in the abdomen often only on one side.
- Bloated or protruded abdomen.
- Painful menstruation.
- Pain in the lower back or thighs.
- Painful intercourse.
- Tenderness of breasts.
- Frequent urination.
- Bowel issues.
- Abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Abrupt weight gain.
Signs of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids start as small as apple seeds and grow as large as a grapefruit. Its symptoms include:
- Pain in the pelvis.
- Bloated or protruded abdomen.
- Heavy menstruation leads to anaemia.
- Frequent urination.
- Enlarged abdomen.
- Rectal pressure.
Both fibroids and cysts cause excruciating pain in the pelvis and bloating of the abdomen. One of the determining factors to differentiate between the two is the type of pain. For instance, abdominal pain only on one side is more likely due to a cyst. On the other hand, heavy menstrual bleeding is more likely due to uterine fibroid.
In addition, both abdominal pain and menstrual bleeding may also be due to other medical conditions. Hence, visiting your doctor at the earliest and commencing either ovarian cyst treatment or fibroid treatment is essential to safeguard your overall health.
What Are the Causes of Cysts and Fibroids?
Fibroids and cysts can occur at any stage in your life. Fibroids are more common during the 40s and 50s and tend to grow in clusters. Although the exact cause is unknown, fibroids may be triggered by:
- Family history.
- Obesity.
- Diet.
On the other hand, ovarian cysts may be caused by:
- Hormonal issues.
- Endometriosis.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome.
- Pelvic infection.
- Pregnancy.
To Sum It Up
Uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts refer to abnormal growths on the uterus and ovaries, respectively. Although both conditions may show mild symptoms in the beginning, it may warrant emergent treatment if symptoms go unnoticed. Hence, it is always a better idea to get yourself examined frequently and get the required treatment for the same.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Which is more dangerous, a cyst or a fibroid?
An ovarian cyst is more dangerous than a fibroid due to its chances of malignancy or turning cancerous.
2) Can you get pregnant with fibroids and cysts?
Fibroids of larger size may not directly affect pregnancy but these may obstruct the fallopian tubes and restrict the space for growing foetus. Similarly, if the ovarian cysts are also linked to endometriosis, it may affect pregnancy.
3) What is the common treatment for ovarian cysts?
Surgery is usually the cornerstone of ovarian cysts. Depending on the size, the cysts can also be removed with laparoscopic surgery.